
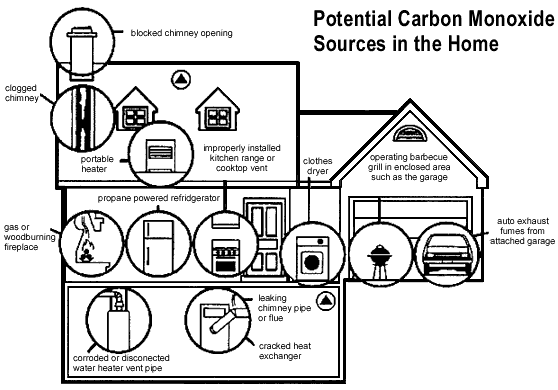

Sources of COġ) Endogenous production: CO is produced endogenously as result of human metabolism of hemoglobin. In the USA, third most frequent cause of accidental death is CO poisoning, most of which (57%) were due to inhalation of exhaust gases. In our country, CO poisoning is most frequently seen during winter months, especially during windy weather, as accident in the home due to inappropriate heating methods. In cases of poisoning by industrial chemicals, CO is the most common (11%) after inhalation of thinner (31%). Average of 4% to 10% of all cases of poisoning occur during childhood, and 58% to 75% of deaths due to poisoning are caused by CO inhalation. It has been reported to be the most frequent cause of fatal poisoning, with an incidence rate of 31%. In this review, clinical data and current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches concerning CO poisoning are discussed.ĬO is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-irritating gas present in the environment even when there is no fire or smoke. It is administered through a mask in the form of normobaric oxygen therapy or through specific devices in the form of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Symptoms must be associated with cause of poisoning, and careful anamnesis and treatment must be conducted quickly. Poisoning in infants has a more severe course than seen in other age groups. In pregnant women, fetus can be harmed with relatively low level of COHb. Depending on severity of exposure, seizures, syncope, and arrhythmia may also be observed. Most common poisoning symptoms are weakness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and nonspecific flu-like symptoms, like vomiting. Clinically, although it affects all organ systems, involvement of central nervous system (CNS) and cardiovascular system is predominant. Although symptoms of acute poisoning are most commonly observed in patients admitted to emergency rooms, effects of chronic exposure to CO can also seen. In addition, it has direct effect of causing cellular damage. CO reacts with oxygen, creating carboxy hemoglobin (COHb), which leads to tissue hypoxia. As CO is a substance that is not visible and has no taste or smell and is therefore difficult to detect, the gas can be a “silent killer” that is not noticed until effects develop. Although most poisonings occur accidentally, some cases are suicide attempt. In our country, it occurs particularly during winter as a result of leak from stove or water heater, or as result of inhalation during a fire. Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is one of the most common types of poisoning causing death worldwide.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
