
A CXR can be used to identify the pacemaker model, as most pacemakers have an X-ray code which is visible on a standard CXR. CXR: evaluate lead position and look for lead fracture.12-lead ECG - any sign of myocardial ischaemia, arrhythmias or abnormal sensing.Blood tests: electrolytes, coagulation screen, digoxin levels if appropriate, myocardial injury markers - eg, troponins (may indicate recent myocardial infarction but may also indicate perforation).Wrong position requiring repositioning.Septicaemia (especially staphylococcal infection).Ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation.Venous thrombosis - rare and usually presents as unilateral arm oedema.Lead dislodgement - usually occurs within two days following implantation of a permanent pacer and may be seen on chest radiography (if the lead is floating freely in the ventricle, malignant arrhythmias may develop).
#VENTRICULAR PACED FAILURE TO CAPTURE SKIN#


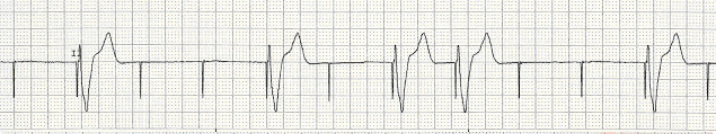
Oversensing: pacer incorrectly senses electrical activity and is inhibited from correctly pacing.This may be due to lead fracture, lead dislodgement, a break in lead insulation, an elevated pacing threshold, myocardial infarction at the lead tip, certain drugs (eg, flecainide), metabolic abnormalities (eg, hyperkalaemia, acidosis, alkalosis), cardiac perforation, poor lead connection at the take off from the generator, and improper amplitude or pulse width settings. Failure to capture: pacing spike is not followed by either an atrial or a ventricular complex.This may be due to battery failure, lead fracture, a break in lead insulation, oversensing (inhibiting pacer output), poor lead connection at the take off from the pacer, and 'cross-talk' (ie a phenomenon seen when atrial output is sensed by a ventricular lead in a dual-chamber pacer). Failure to output: no pacing spike is present despite an indication to pace.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
